Each process may involve one or more activities, as required by outputs. In this case, the 20-ounce box has the lower unit price, making it the more cost-effective choice. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
Financial Efficiency Ratios (Revision Presentation)
In a manufacturing company, calculating these figures may be a little tricky but it becomes difficult in case of the service industry as it is difficult to identify a unit for services rendered. Activity-based costing helps in allocating cost to activities that are value-added. It also improves operational efficiency and enhances decision-making through better, more meaningful cost information. Let us understand the differences between a cost per unit equation and price per unit through the comparison below.
Breakeven Analysis
One of those cost profiles is a variable cost that only increases if the quantity of output also increases. While a fixed cost remains the same over a relevant range, a variable cost usually changes with every incremental unit produced. Because variable costs scale alongside, every unit of output will theoretically have the same amount of variable costs. Therefore, total variable costs can be calculated by multiplying the total quantity of output by the unit variable cost. Private and public companies account for unit costs on their financial reporting statements. All public companies use the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) accrual method of reporting.
Differences Between Cost Center and Cost Unit
- This calculation determines the number of units a company needs to sell to cover all its costs.
- Allocating costs to specific units or products might involve assumptions that don’t accurately represent the actual consumption of resources.
- Activity-based costing encourages managers to identify which activities are value-added—those that will best accomplish a mission, deliver a service or meet customer demand.
- For others who are tied to an hourly job, putting in more direct labor hours results in a higher paycheck.
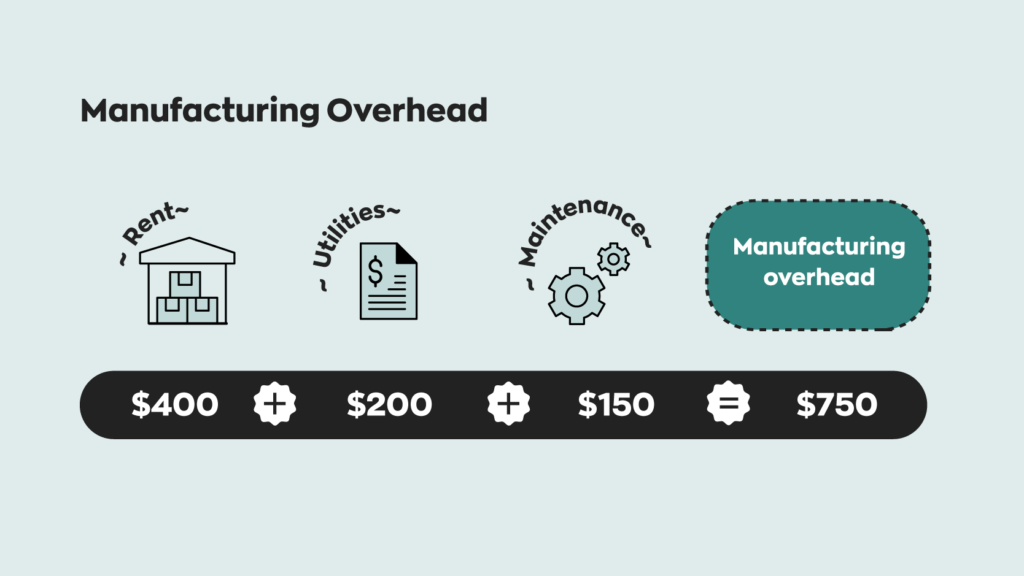
If a business increases production or decreases production, rent will stay exactly the same. Although fixed costs can change over a period of time, the change will not be related to production, and as such, fixed costs are viewed as long-term costs. Examples of fixed costs are rent, employee salaries, insurance, and office supplies. A company must still pay its rent for the space it occupies to run its business operations irrespective of the volume of products manufactured and sold. Generally, companies consider different factors while determining the selling price for their products keeping in view all the fixed and variable expenses. Traditional cost accounting typically uses a single overhead rate based on machine hours, labor hours, or some other measure of production volume.
Variable Cost vs. Average Variable Cost
Fluctuations in sales and production levels can affect variable costs if factors such as sales commissions are included in per-unit production costs. Meanwhile, fixed costs must still be paid even if production slows down significantly. You can find a company’s variable costs on their balance sheet under cost of goods sold (COGS). This measures the costs that are directly tied to production of goods, such as the costs of raw materials and labor.
Company and Support
It appears on the company’s financial statements and is crucial in determining the market price of the company’s product or service. It is also used by investors to decide whether or not a company is a good investment, as it helps to determine the company’s profitability. Unit Cost is the total cost (fixed and variable) incurred by the company to produce, store and sell one unit of a product or service. This concept is most commonly used in the manufacturing industry and is calculated by adding fixed and variable expenses and dividing it by the total number of units produced.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Unit cost is arrived at by combining the variable and fixed costs and dividing by the total number of units produced. For example, assume total fixed costs are $40,000, total variable costs are $20,000, and you produced 30,000 units. You calculate the total cost of production by adding the how revenue affects the balance sheet $40,000 fixed costs to the $20,000 variable costs for a total of $60,000, then divide $60,000 by 30,000 to get the unit cost of $2. Cost per unit equation is a crucial metric in evaluating financial performance. It provides insights into the efficiency of production or service delivery.
The analysis provides the foundation for creating realistic budgets and projections. It allows you to anticipate expenditures and revenue streams with greater precision. It fosters financial stability and aids in proactive resource allocation. This article looks at the definition of unit cost and everything you need to know about it. Commissions are often a percentage of a sale’s proceeds that are awarded to a company as additional compensation.